Difference between revisions of "Automatic Gain Control (AGC)"
(→Manual Control) |
(→Manual Control) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
'''AGC Mode''': Manual Control | '''AGC Mode''': Manual Control | ||
| − | '''Max PGA''': | + | '''Max PGA''': Allows the user to restrict the maximum gain of PGA. Can be used in very noisy environments when noise is greater than the set noise threshold so as not to amplify the noise too much. |
'''Attack Time''': This determines how quickly the AGC circuitry decreases the PGA gain when the input signal exceeds the target level. | '''Attack Time''': This determines how quickly the AGC circuitry decreases the PGA gain when the input signal exceeds the target level. | ||
It is expressed in fractions of ADC sampling rates. | It is expressed in fractions of ADC sampling rates. | ||
| − | '''Decay Time''': | + | '''Decay Time''': This determines how quickly the AGC circuitry increases the PGA gain when the input signal falls below the target level. |
| + | It is expressed in fractions of ADC sampling rates. | ||
'''Gain Hysteresis''': | '''Gain Hysteresis''': | ||
| − | '''Hysteresis''': | + | '''Hysteresis''': Hysteresis around the noise threshold avoids fluctuation of ADC output between target and no signal when the signal is around noise threshold. |
| + | So the signal around noise threshold, it has to rise above the hysteresis to be amplified to target level. | ||
| + | Reverse if a signal is around noise threshold, it has to fall below hysteresis to be considered as noise and set to 0db. | ||
| − | '''Noise Debounce''': | + | '''Noise Debounce''': If the signal level falls below noise threshold level, it has to stay there for a time greater than Noise debounce time, only then the ADC output is set to 0 to avoid false noise artifact effects. |
| − | '''Noise Threshold''': | + | '''Noise Threshold''': A threshold used to differentiate noise from very weak signals so that the PGA does not amplify the noise also. |
| + | So if the signal is below this reference, it is considered as noise and the output of ADC is 0 db. | ||
| − | '''Signal Debounce''': | + | '''Signal Debounce''': If the signal level goes above the noise threshold level, it has to stay there for at least Signal debounce time to allow PGA to switch to target level to prevent false switching. |
'''Target Level''': This represents the nominal output level that the AGC attempts to hold the ADC output signal. It is expressed relative to full scale range of the ADC range (in db) so it is recommended that the target level be set with enough margin to avoid clipping of loud signals. | '''Target Level''': This represents the nominal output level that the AGC attempts to hold the ADC output signal. It is expressed relative to full scale range of the ADC range (in db) so it is recommended that the target level be set with enough margin to avoid clipping of loud signals. | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 26 September 2017
This article explains the Automatic Gain Control (AGC) function in Exigo.
By enabling AGC gain will be automatic adjusted according to the background noise level.
AGC can be enabled on Access Panels and Kits.
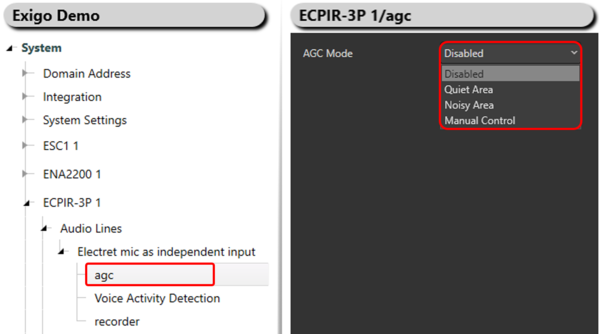
Configuration
Enabling AGC:
- Desired endpoint -> Audio Lines -> Electret mic as independent input -> agc
There are 4 different AGC Modes:
- Disabled
- Quiet Area
- Noisy Area
- Manual Control
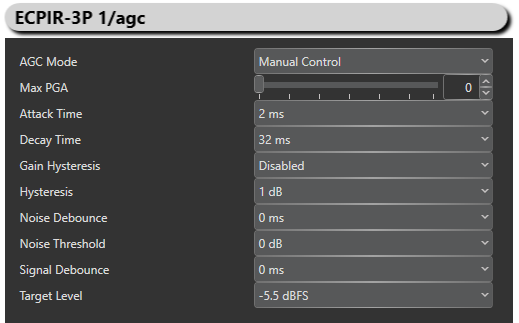
Manual Control
With manual control it is possible to adjust several parameters to get the optimal AGC needed.
AGC Mode: Manual Control
Max PGA: Allows the user to restrict the maximum gain of PGA. Can be used in very noisy environments when noise is greater than the set noise threshold so as not to amplify the noise too much.
Attack Time: This determines how quickly the AGC circuitry decreases the PGA gain when the input signal exceeds the target level. It is expressed in fractions of ADC sampling rates.
Decay Time: This determines how quickly the AGC circuitry increases the PGA gain when the input signal falls below the target level. It is expressed in fractions of ADC sampling rates.
Gain Hysteresis:
Hysteresis: Hysteresis around the noise threshold avoids fluctuation of ADC output between target and no signal when the signal is around noise threshold. So the signal around noise threshold, it has to rise above the hysteresis to be amplified to target level. Reverse if a signal is around noise threshold, it has to fall below hysteresis to be considered as noise and set to 0db.
Noise Debounce: If the signal level falls below noise threshold level, it has to stay there for a time greater than Noise debounce time, only then the ADC output is set to 0 to avoid false noise artifact effects.
Noise Threshold: A threshold used to differentiate noise from very weak signals so that the PGA does not amplify the noise also. So if the signal is below this reference, it is considered as noise and the output of ADC is 0 db.
Signal Debounce: If the signal level goes above the noise threshold level, it has to stay there for at least Signal debounce time to allow PGA to switch to target level to prevent false switching.
Target Level: This represents the nominal output level that the AGC attempts to hold the ADC output signal. It is expressed relative to full scale range of the ADC range (in db) so it is recommended that the target level be set with enough margin to avoid clipping of loud signals.
Availability
This function is available from Exigo 1.3.3 and newer.